Solar power is considered the solution to many problems we are facing now – from the degradation of the environment, carbon footprint, and climate change to saving money, freedom from the grid, and creating jobs.
Solar energy is free. And, it is available almost everywhere. All we need to have is the setup to tap the energy and convert it into a usable form. This is exactly what solar panels do for us.
Let us see in detail how solar panels accomplish these tasks.
Solar panels for homes – An overview
A home solar panel is an arrangement of PV cells that help in harnessing the energy from the sunshine and convert it into electricity. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect. The electrical energy generated is direct current (DC).
This DC electricity has to be converted to alternating current (AC) using a solar inverter to make it useful for us. The converted AC electricity is allowed to flow into the home electrical system for use by various appliances and devices.
Here is a step-by-step account of how residential solar panel systems work.
- Step 1. PV cells absorb energy from the sunshine and convert it into DC electricity.
- Step 2. The DC electricity generated by individual PV cells flows into an inverter which converts it into AC electricity.
- Step 3. The inverter is connected to the home electrical system, thus allowing the AC electricity generated to power the appliances and devices.
- Step 4. The excess electricity, if any generated, is stored in a battery for later use or fed to the main grid for credits or payment.
Now, let us start from the beginning and understand the technical terms, the functions of various components, and how all of them work in conjunction to power your home.
What is solar energy?
The sun is the ultimate source of energy for us. The sunshine does more than provide us with light in the daytime and helps in warming the earth and the atmosphere. The heat and light energies present in the sunlight is known as solar energy.
It is estimated that if we manage to harness all the solar energy falling on the surface of the earth for an hour, it would be enough to meet the global power needs for a year.
The sun is a star and like the stars in our galaxy, functions as a massive nuclear reactor. Solar energy is produced from a process happening in its core called nuclear fusion. The energy thus generated goes out as radiation from the surface of the sun into space. This radiation or sunlight is made up of photons or small units of solar energy. This solar energy also reaches the earth.
What is a solar panel?
The solar panel is an informal term used for a photovoltaic module or PV module. It is a collection of photovoltaic cells mounted on a framework. Each PV cell converts the solar energy falling on it into direct current electricity using the photovoltaic effect.
Each solar cell is a sandwich of two slices of semiconducting material like silicon. To generate electricity, the cells should create an electric field by separating the opposite charges. To make this possible, the two slices are induced positive and negative charges by introducing other substances.
Typically, the top silicon layer is seeded with phosphorus to add extra electrons to make it negatively charged. The bottom silicon layer is sowed with boron which has fewer electrons, thus making it positively charged.
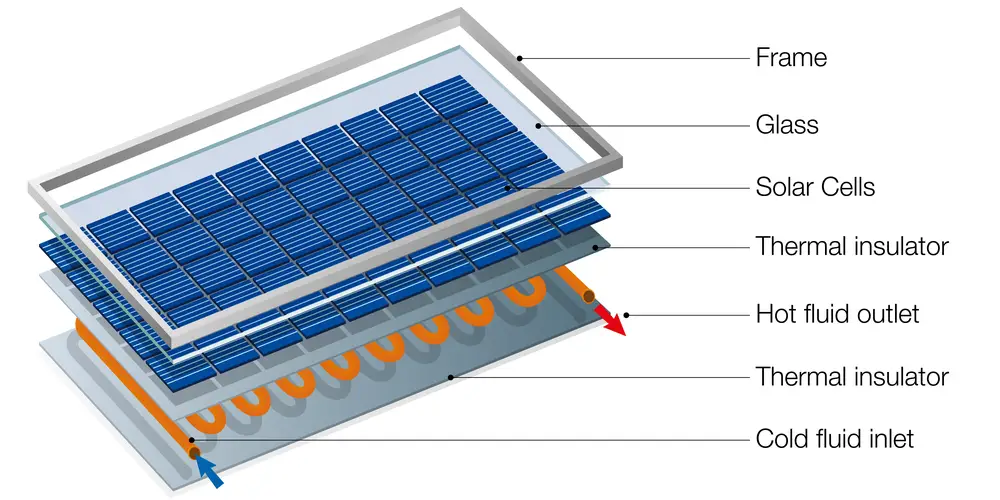
The PV cells are arranged in a grid-like pattern in a solar panel to ensure maximum exposure to the sunshine. The solar panels are mounted on a metal and glass casing. A layer of anti-reflective coating is added to the surface of the solar cells to increase their efficiency in absorbing the sunlight.
The cells are made of a photovoltaic substance like crystalline silicon. The silicon used in them comes with different structures – monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and amorphous forms.
The cells made from monocrystalline silicon are the most efficient and the most expensive of the three. Amorphous silicon cells are used in thin-film, flexible solar panels.
What is the photovoltaic effect?
The photovoltaic effect was discovered by Edmond Becquerel in 1839. When two layers of semiconductors carrying opposite charges are joined together at a junction, an electric field is established.
When a PV cell is exposed to sunshine, the photons or small packets of energy present in it is absorbed by the cell. The energy from the photon is transferred to the electrons present in it, thus raising its energy level. As the excited electrons break free of the atomic bond and start moving freely, it leaves behind a ‘hole’.
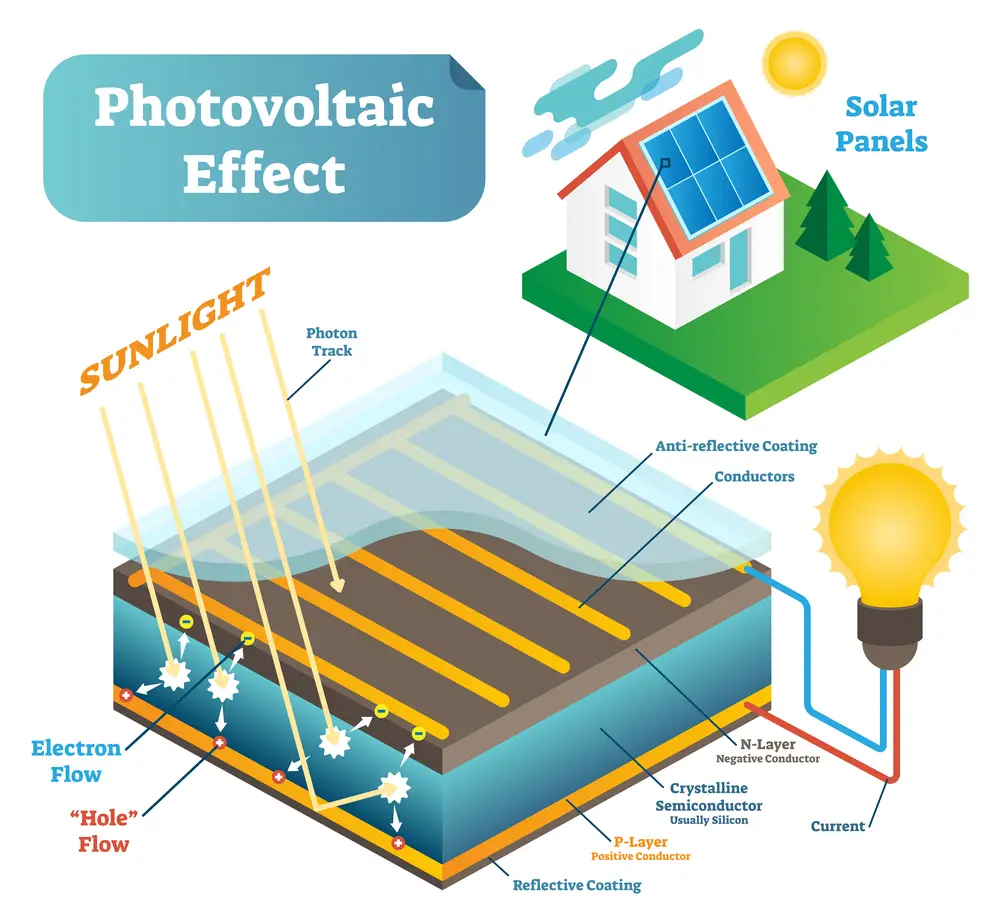
The negatively charged electrons and positively charged holes flow in the opposite direction. While electrons flow to the negative side, the holes move to the positive side, creating a current.
Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to convert solar energy into electrical energy.
How does solar energy work?
When sunlight hits the solar cell, the photons present in it dislodge the electrons in the atoms of the solar cell. The conductors attached to the positive and negative sides of the unit constitute an electrical circuit. The electrons that are knocked free flows through this circuit, generating electric current.
To make this flow of electrons or electricity in each unit into a usable form, more work needs to be done. The metal conductors placed on the sides of each solar cell captures this flow of electrons and transfers them into the attached wire. The electricity flowing into the wires from the various units in a panel is direct current (DC).
How do solar panels meet our electricity needs?
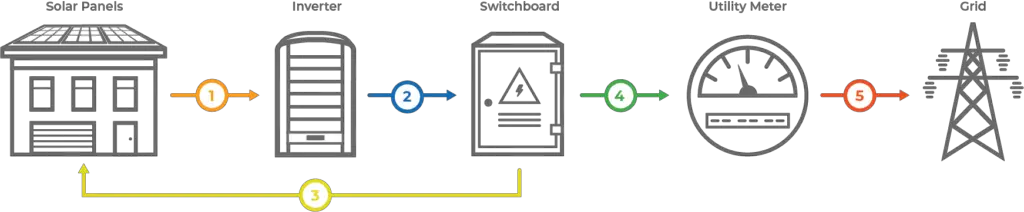
The electricity generated by solar panels is direct current or DC. This is not suitable for use in home appliances and devices. This needs to be converted to alternating current or AC to be of usable form. An inverter connected to the solar power installation accomplishes this task.
The alternating current produced by the inverter is fed into the main electrical switchboard. From here it reaches the various devices and appliances in the home.
The excess power generated may be stored using a battery or fed into the main grid for credit or payment. Selling extra power generated to the grid requires an arrangement called net metering. Net metering requires a bi-directional utility meter that can measure the inflow and outflow of electricity.
Do solar panels generate electricity on cloudy and rainy days?
PV panels can generate electricity with direct or indirect sunshine, though their efficiency is at the maximum when exposed to direct sunshine. This means even on cloudy days, if the solar panels receive reflected light, they will continue to produce electricity, albeit less.
Rains are in fact good for PV panels, as it washes away the accumulated dirt and dust on their surface. For the solar panels to function at their optimal level, they need to be cleaned at regular intervals. The presence of dirt and dust can form a barrier, reducing the absorption of sunlight by the cells.
At night, when there is no sunshine, the solar panels cannot generate electricity.
Benefits of solar energy
Solar power comes with vast benefits. Some of the notable ones are:
1. Environment-friendly
Solar power systems tap the free energy from the sun that is abundantly available almost anywhere in the world. It helps in reducing our dependence on the grid energy generated using fossil fuels. Installing a solar energy system will help in our fight against climate change and global warming by bringing down greenhouse gas emissions.
While burning fossil fuels for generating electricity causes air and water pollution, solar energy is considered clean and green energy for its minimal impact on the environment. Water conservation is another area in which solar power scores big against traditional electricity generation.
2. Reduce or eliminate electricity bill
Depending on the size of solar power installation and the availability of sunshine, you will be able to bring down your dependency on grid energy, thus reducing the electricity bill. In areas with round-the-year sunshine, it is possible to bring the bill amount to zero.
Even with a battery to store excess electricity generated and/or a backup like a diesel generator for emergencies, it is still a good option to remain connected to the grid. Using the net metering arrangement, you can export the extra electricity generated for credits and use grid energy at night or when your electricity generation is falling short of demand.
3. Tax credits and incentives
To promote the installation of solar power in homes, the authorities are offering a slew of incentives. The most prominent among them is the federal income tax credit. The solar investment tax credit or ITC offers 26% tax credit for solar systems installed in residential and commercial properties.
The delay in the phasedown of the tax credit is a big advantage for residential solar power users.
4. Protection from rising electricity rates
The lifespan of a solar power installation is 20-25 years. And, once the installation is done, the cost of maintenance and repairs is minimal. This means the cost of electricity generation remains almost fixed during its lifetime.
Compare this to the ever-increasing rates for grid power. It is not difficult to get the picture.
Limitations and disadvantages of solar energy
It is rare to come across something that has only positives and no negatives. Solar power also comes with a few disadvantages.
1. Upfront cost
One of the most prominent deterrents for the installation of solar power systems is its prohibitive cost. As newer technologies emerge, the cost has come down substantially in the last decade.
Location and weather dependent
Availability of direct sunshine round the year can make solar power the most profitable. However, sunlight is a luxury in many locations. Even in places with good sunshine, it may not be available throughout the year. This means it is not possible to depend on solar energy completely in such places.
2. High cost for storage
The extra electricity generated can be stored using batteries for use at nighttime or when the system is underperforming. However, this setup doesn’t come cheap. This drawback can be overcome by a net-metering arrangement.
Require space for hosting solar panels
The more your energy needs are, the more solar panels are needed and the more space to keep them. Rooftops are the ideal places for solar panels but if your roof doesn’t have adequate space, you may have them in the yard provided there is enough sunshine.
3. Manufacturing involves pollution
Though solar energy is free and clean, harnessing it leads to pollution and carbon footprint. Manufacturing solar panels involve hazardous materials that can result in pollution, if not done in the right way. Moreover, transportation and installation of solar panels lead to some greenhouse gas emissions.
What is the average cost of a solar power system?
The short answer is ‘It depends’.
The longer version goes something like this.
The cost of installing a home solar system depends on several factors including the energy requirement, brand, and location. Location matters because many of the incentives offered are state-specific.
To quote EnergySage in this matter, “Solar panel costs for a 10-kilowatt (kW) installation in the U.S. ranges from $17,760 to $23,828 after the federal solar tax credit, and the average price per watt for solar panels ranges from $2.40 to $3.22”.
In addition to this, incentives offered by states and brands can bring this estimate further down.
Yes, the upfront cost of stand-alone solar panels is high. There are other options to derive the benefit of solar power for homes without the outright purchase of the equipment. You may opt for shared or community solar, solar leases, Power Purchase Agreements (PPA), or Solarize Programs.
What are its maintenance requirements?
Not much. And, that is the second-best aspect about solar power after the fact that it is free. The average lifespan of solar panels is 20-25 years. That says a lot about the upkeep it requires.
The surface of the solar panels has to be kept clean to help them function at an optimal level. This means washing away the accumulated dirt and dust periodically. The efficiency of the solar panels may come down as years pass by.
However, the story is different for the solar inverter attached to the system. It needs to be replaced a few times during the lifetime of the solar system. The newer micro-inverters attached to each solar panel is said to be as long-lasting as the panels themselves.
Bottom line
Now we are faced with the question – after all the effort and expenditure of installing a solar power system in your home, is it worth it? Do solar systems save money?
20 or 25 years is a long time in terms of a lifetime for any equipment. Even with small savings per month, it is estimated that the system will pay for itself in 7-8 years. You may consider the remaining years as a bonus.
Again, the savings on the energy bill depends on the availability of sunshine, the size of the system, and the energy rate in your area among others.
Recommended Reading:

